Describe the Structural and Functional Properties of Cardiac Muscle
Rhythmicity means the ability of the heart to beat regularly without external stimulation. Cardiac muscle varies from the skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and not under voluntary control.

Cardiac Muscle Definition Function Structure Britannica
Start your trial now.

. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscles in the human body- the others being visceral and cardiac muscles. For each of the following state whether it applies to skeletal muscle cardiac muscle or both. Pump blood away from the heart towards the lungs and throughout the body.
It is myogenic in origin not neurogenic. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Cardiac muscle tissue structural properties.
Properties of Cardiac Muscle. -cells are separated by intercalated discs. Briefly describe the events of cardiac muscle cell contraction.
Cardiac muscle cannot be stimulated while it is contracted because its excitability during contraction is zero due to long absolute refractory period so it cannot be tetanized. These inner and outer layers of the heart respectively surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. It contains cardiac muscle cells which perform highly coordinated actions that keep the heart pumping and.
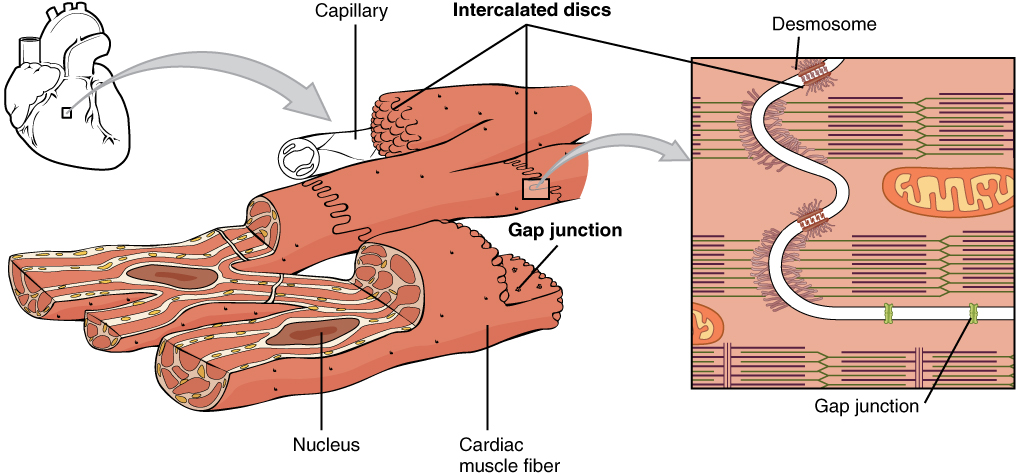
Cardiac muscle only exists in the heart. The overlapping region in each cell forms finger-like extensions in the cell membraneThese structures are called as intercalated disksThe structure of the intercalated disk forms gap junctions and desmosomes between the two cells allowing the passage of electrochemical. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells.
In this lesson skeletal muscles its definition structure properties functions and types are explained in an easy and detailed manner. The nature of the heart muscle is to communicate fiber to fiber so that each. In that it possesses the contractile units called sarcomeres.
Starlings law of the heart Length-tension relationship. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Degree of stretch of cardiac muscle cells before they contract Frank-Starling law of the heart Increased venous return distends stretches the ventricles and increases contraction force 2.
First week only 499. Each cardiac muscle cell is in contact with another three or four cardiac muscle cells. This continuous rhythmic activity is a major physiological difference between cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue.
Cardiac muscle fibers also have only one or two nuclei contain more mitochondria have fewer T-tubules and much less. Smooth appearance under a microscope. Well go over the unique features of cardiac muscle tissue.
Cardiac muscle can perform both isometric and isotonic types of contractions. Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. These three muscles collectively make the muscular tissue of the animal body.
--The mitochondria in cardiac muscle fibers are larger and more numerous-cardiac muscle tissue depends largely on aerobic cellular respiration to generate ATP and thus requires a constant supply of oxygen. Cardiac muscle also known as heart muscle is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. Cardiac muscle is dense and packed tightly.
The muscle which forms the contractile elements of the atria and ventricles is highly specialized. The intercellular spaces are filled with a loose connective tissue matrix which is the endomysium containing numerous capillaries. Solution for Describe the structural and functional properties of cardiac muscle and explain how it differs from skeletal muscle.
Cardiac Muscle Definition. The nodal fibres and conducting system are self- excitable. The rhythmic contraction of cardiac.
The muscle fibers are striated and branched and have intercalated discs. Cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. -cells are short branched striated uni- or multi-nucleate.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. In contrast to skeletal muscle cardiac muscle fibers are short fat branched and interconnected. Describe the structural and functional properties of cardiac muscle and explain how it differs from skeletal muscle.
Skeletal muscle smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are made of myofibrils. Along walls of heart. They contain myofibrils consisting of typical sarcomeres.
Cardiac muscle is the same as the skeletal muscle the other major muscle type. Regulated by autonomic nervous system. 100 1 rating Solution Similarities.
Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle another major muscle type in that it possesses contractile units known as sarcomeres. All three muscles are regulated by the nervous system. In lining of internal organs.
Click card to see definition. The hearts role in producing the pressure gradient by which the bodys tissues are perfused with blood means that cardiac muscle is active from about the fourth week of fetal life until death. Properties of cardiac muscle Automaticity capability of contract even in the absence of neural control Rhythmicity heart beats are extremely regular Contractibility cardiac muscle contracts in response to a stimulus Excitability ability of the cardiac muscle to respond to different stimuli.
It plays an important role in making your heart beat. -cardiomyocytes are interspersed with. Same sliding filament mechanism.
This feature however also distinguishes it from smooth muscle the third muscle type. Who are the experts. Describe the structural and functional properties of cardiac muscle and explain how it differs from skeletal muscle.
Briefly describe the events of cardiac muscle cell contraction. Extrinsic factors called inotropic agents mscell contractile strength at a given muscle length independent of muscle stretch and EDV. Tap card to see definition.
Describe the structural and functional properties of cardiac muscle and explain how it differs from skeletal muscle. However these features of cardiac muscle also distinguish it from smooth muscle which is the third muscle type. Like skeletal muscle cardiac muscle is striated and contraction occurs using the.
-Cardiac muscle fibers can also use lactic acid. -cardiac muscle cells are branching striated generally uninucleate cells.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Anatomy And Physiology

Structural And Functional Characteristics Of Cardiac Muscle Tissue And Conduction System Flashcards Quizlet

Comments
Post a Comment